Waste-to-Energy Facility
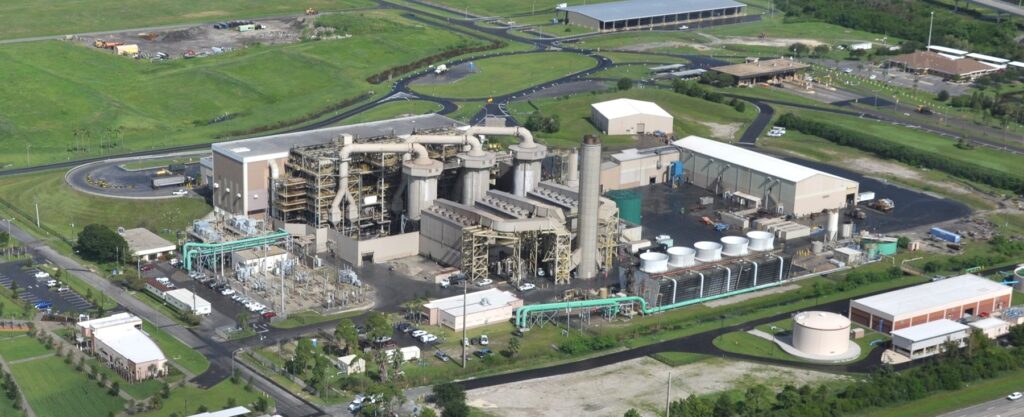

According the Environmental Protection Agency, 75 facilities in the United States recover energy from the combustion of garbage.
Florida has 10 Waste-to-Energy facilities. The Tampa Bay area is home to four Waste-to-Energy facilities, which are located in Pinellas County, Hillsborough County, the City of Tampa and Pasco County.
Without Waste-to-Energy facilities, local governments would be faced with closing existing landfills as they reach capacity and then transferring garbage to regional private landfills at a considerable cost, including transportation and disposal fees.
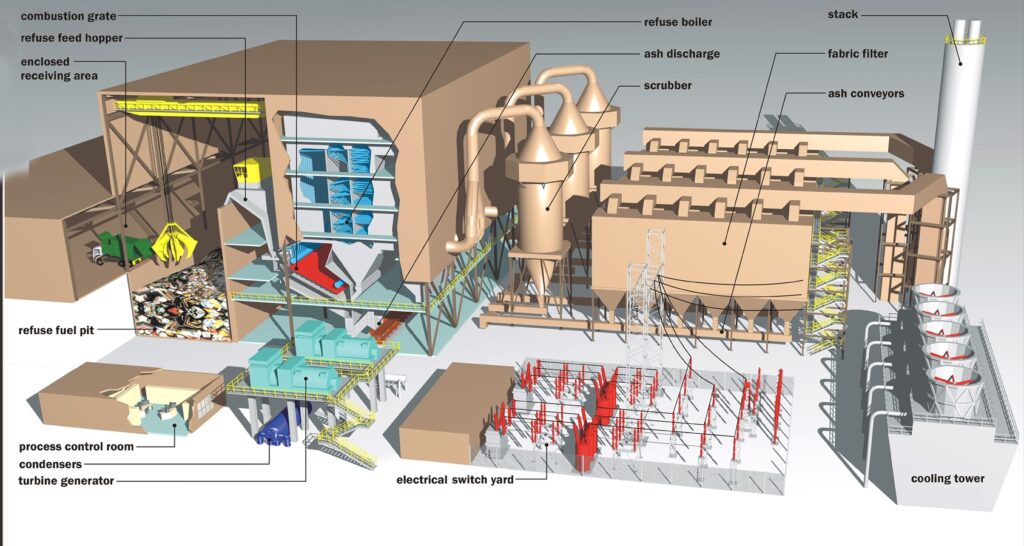
Garbage generated and collected in Pinellas County is sent to the Pinellas County Solid Waste Disposal Complex. The Complex, which is managed by the Solid Waste department, includes a Waste-to-Energy facility (WTE Facility) and landfill. The WTE Facility works like a power plant, except that it uses garbage as fuel and converts garbage into electrical energy.

Garbage is burned to create up to 75 megawatts (MW) per hour of electricity, which is the equivalent of powering 45,000 homes and businesses each day. The generated heat boils water to create steam, which is sent to a turbine generator to make electricity. The WTE Facility uses some generated electrical energy to power its operating equipment. The remainder of the electrical energy, in excess of 60 megawatts, is sold to Duke Energy. Revenues from the sale of the electricity help offset the cost of operation.
Although electricity production is important, the primary function of the WTE Facility is to reduce the volume of incoming garbage.
Just as firewood in a campfire is reduced to ash, when burned, garbage reduces in volume by 90% (the weight is reduced by 75% because the remaining residue is comprised of metals, non-combustible items and ash). Metals are recycled and the ash is landfilled in Bridgeway Acres Landfill.
Fun facts about the WTE Facility:
- Pinellas County opened the WTE Facility in 1983 with two boilers and one turbine generator
- A 3rd boiler and second turbine generator were added in 1986
- The storage pit can hold up to three days’ worth of garbage
- The WTE Facility burns an average of 2,700 tons per day
- Waste burns in the range of 2,000°F to 2,200°F
- Approximately 60 million pounds of metal is recovered from the remaining combustion residue and recycled each year
- Sophisticated combustion and air pollution control systems clean the gas created when garbage is burned. The gas is monitored continually to make sure it complies with and does not exceed state and federal regulations
Ash Used as Landfill Cover
Even when the WTE Facility is running at full capacity, 200-300 tons of garbage is still landfilled daily. State of Florida regulations require the landfilled waste to be covered each day to eliminate vectors and odors. The Solid Waste department has a state-approved landfill operations plan that allows the ash from the WTE Facility to be used as as daily cover. This avoids depleting natural resources, like soil, while reducing operation costs and remaining in compliance with state and federal environmental regulations.
Renewable Energy Credits (RECs)
Renewable energy credits (RECs) are equivalent to 1 MWh of electricity generated from a renewable energy resource. Examples of renewable energy include WTE, wind, solar, geothermal, and hydropower.
A REC certificate certifies that the energy was exported into the shared system of power lines (i.e., the grid) that transport energy. An entity that buys the REC certificate demonstrates that they are taking credit for using renewable energy.
The Solid Waste department’s WTE Facility energy is certified as renewable energy by an independent, industry-recognized entity and posts the REC certificates for purchase. Commodity brokers purchase the REC certificates on behalf of their clients. The purchased REC certificates demonstrate that the purchaser has reduced their carbon footprint and contributed to their sustainability program. The WTE Facility generates approximately 440,000 MWh (RECs) per year.
WTE in the Community
In 2020, the Solid Waste department released a Solid Waste Master Plan that evaluated the County’s existing solid waste management system and provided solutions to improve recycling, diversion, operations, programs, facilities and technologies. The Master Plan includes 28 key strategies that support the County’s vision of Zero Waste to Landfill by 2050. The WTE Facility helps the County reach this vision by reducing the volume of incoming garbage, which helps extend the life of the county’s one and only landfill.
In 2021, the WTE Facility reduced nearly 1.2 billion pounds of garbage by 90 percent of its volume and generated enough electricity to power the equivalent of 45,000 single family homes per day while recovering and recycling the equivalent amount of metal in approximately 19,000 automobiles from the incineration process.
In summary, WTE facilities are, by far, the most effective alternative to landfill disposal, while generating a revenue stream that funds the entire solid waste management system operation and reserves for future capital projects. Some of these reserves were reinvested into the WTE Facility to restore it to like-new operating condition and extend its life an additional 25 years.
Learn More
While the WTE Facility is critical to reducing the volume of garbage, there are important steps that you can take to prevent waste from being created and sent for disposal.
- Learn about the Waste Management Hierarchy and ways that you can help reduce, reuse, and recycle at home, work and play in Pinellas County and the greater Tampa Bay area
- Request to take a tour of the Solid Waste Disposal Complex
Additional Resources
- Where Does It Go? Search Tool
- Recycle Guide & Downloadable Signage
- Household Chemical Collection
- Collection: Garbage & Recycling
- Hours: Solid Waste Disposal Complex
- Disposal Fee Information
- Educational Resources: Garbage and Recycling
- Recycling FAQ
- Map of Recycling Drop-Off Centers
- Artificial Reef Program
- Mulch Pickup Program
- For Businesses: Garbage & Recycling Resources
- How Mixed Recycling Works In Pinellas County
- Video Library: Garbage and Recycling
- Holiday and Gift-Giving Guide
- Pinellas Partners in Recycling
- Waste-to-Energy Facility
- Bridgeway Acres Landfill
- Solid Waste Master Plan
- Solid Waste Disposal Accounts
- Lealman Garbage and Recycling Collection
- Tampa Bay Recycles
- Why Recycling Is Important
- Discover Careers with Pinellas County Solid Waste
Updated on March 6, 2024.